Alphabestiary D — Denis Diderot
The Seventeenth Century produced in Europe giants of science and philosophy and brought to birth the beginnings of Western Modernism. Their names are a pantheon of luminaries: Francis Bacon; Galileo Galilei; Thomas Hobbes; Rene Descartes; Blaise Pascal; Isaac Newton; Johannes Kepler; Gottfried Wilhelm Leibnitz; Baruch Spinoza; John Locke — names that mark the foundations of the culture we now live in.
But during their lifetimes, their pioneering work remained the province of a rare sliver of humankind, those others of their intellectual gift who could understand and appreciate their thought. The mass of European population remained illiterate, and subject to centuries-old traditions and institutions of monarchy and religion. It wasn’t until the next century that the dam broke and the results of rationalism and empiricism made a wide splash in society, in a movement that self-congratulated itself as The Enlightenment.
And in the center of it all, in France, was Denis Diderot, one of the so-called “philosophes,” a group of writers and thinkers advocating secular thinking, free speech, the rights of humans, the progress of science and technology, and the general betterment of the human condition.
Among the philosophes were Voltaire, Montesquieu, Abbé de Mably, Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Claude Adrien Helvétius, Jean d’Alembert, the Marquis de Condorcet, Henri de Saint-Simon, and the Comte de Buffon. They wrote about science, government, morals, the rights of women, evolution, and above all, freedom of speech and freedom from dogma. They advocated the expansion of knowledge and inquiry. And they didn’t write merely for other intellectuals, but for a wider, middle-class literate readership. It was a blizzard of books, pamphlets and magazines.
Denis Diderot was born in 1713 in the Champagne region of France, the son of a knife-maker who specialized in surgical equipment. His father expected him to follow in the family business, but Diderot first considered joining the clergy before studying for the law and by the early 1740s, had dropped out to become a professional writer, a metier that paid little and brought him into conflict with the royal censors with notorious frequency.
He translated several works, including a medical dictionary, and in 1746, he published his Pensées Philosophiques (“Philosophical Thoughts”), which attempted to reconcile thought and feeling, along with some ideas about religion and much criticism of Christianity.
He wrote novels, too, including in 1748, the scandalous Les Bijoux Indiscrets (“The Indiscreet Jewels,” where “jewels” is a euphemism for vaginas), in which the sex parts of various adulterous women confess their indiscretions to a sultan who has a magic ring that can make vaginas talk.
His most famous and lasting novel is Jacques le Fataliste et son Maître (“Jacques the Fatalist and his Master”), from 1796, a picaresque comedy in which the servant Jacques relieves the tedium of a voyage by telling his boss about various amorous adventures.
But Diderot is remembered primarily for his work on the Encyclopédie, which he edited along with Jean le Ronde d’Alembert, and for which he wrote some 7,000 entries. It was published serially and periodically revised from 1751 to 1772 and mostly published outside of France and imported back in — censorship was strict and many books were published in the Netherlands or Switzerland to avoid French government oversight.
In fact, Diderot spent some months in prison for his work on the Encyclopédie.
There had been earlier attempts at encyclopedias, including Ephraim Chamber’s Cyclopedia, or an Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences published in London in 1728, and John Harris’ 1704 Lexicon Technicum: Or, A Universal English Dictionary of Arts and Sciences: Explaining Not Only the Terms of Art, But the Arts Themselves. The 18th century wallowed in long book titles.
Among the projects of this age with an appetite for inclusiveness was Samuel Johnson’s Dictionary of the English Language of 1755.
And the idea of binding all of human knowledge up in a single volume goes all the way back to the Naturalis Historia of Pliny the Elder in the First Century CE.
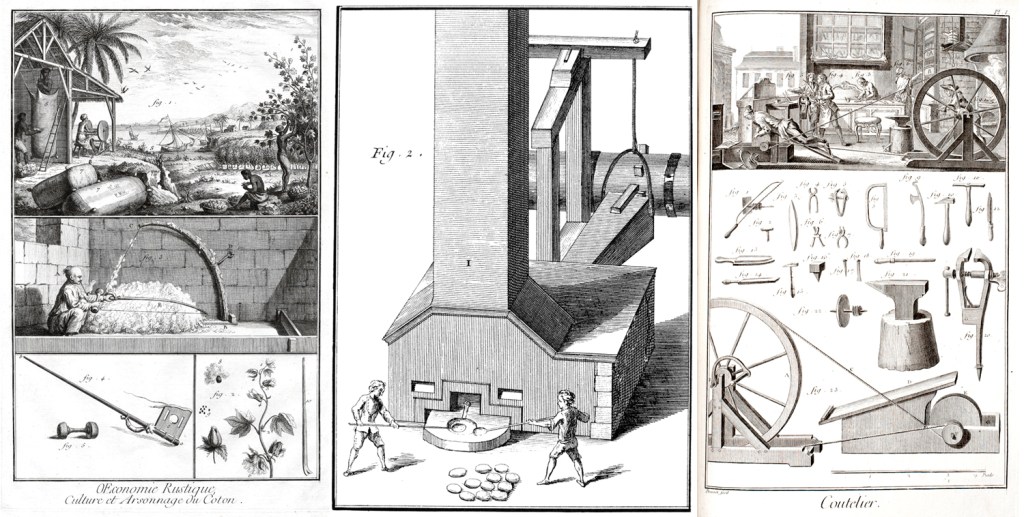
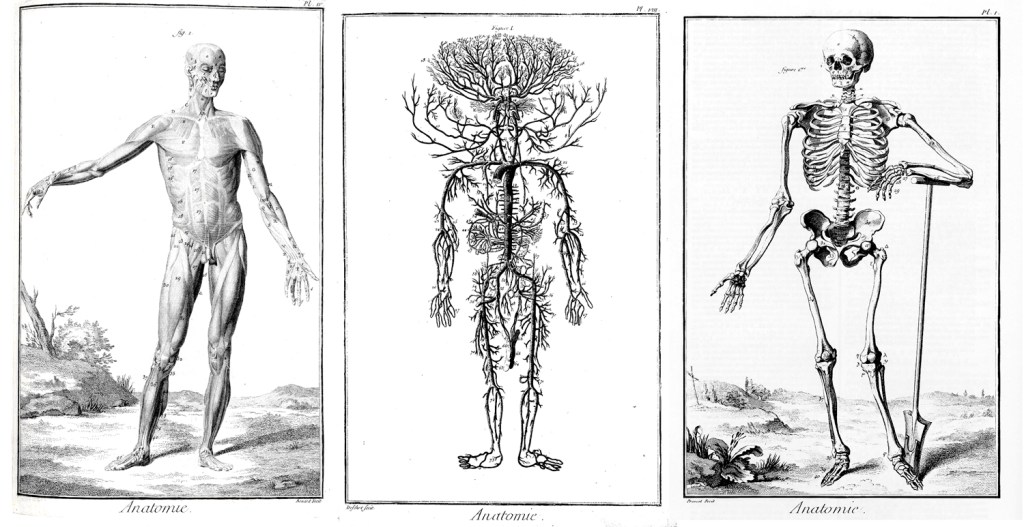
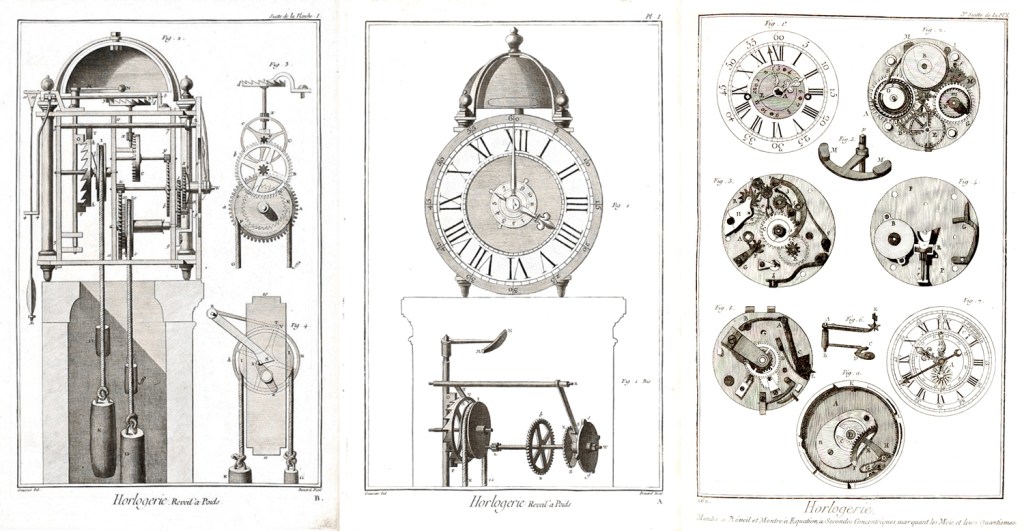
But none of these were as compendious in intent as the French Encyclopédie, which initially ran for 28 volumes and included 71, 818 articles and 3,129 illustrations. It comprised some 20 million words over 18,000 pages of text. It was a huge best-seller, earning a profit of 2 million livres for its investors.
In his introduction, Diderot wrote of the giant work, “The goal of an Encyclopédie is to assemble all the knowledge scattered on the surface of the earth, to demonstrate the general system to the people with whom we live, & to transmit it to the people who will come after us, so that the works of centuries past is not useless to the centuries which follow, that our descendants, by becoming more learned, may become more virtuous & happier, & that we do not die without having merited being part of the human race.”

In the article defining “encyclopedia,” Diderot wrote that his aim was “to change the way people think.”
Their goal was no mean or paltry one, but to encompass everything known to humankind. So that, according to Diderot himself, if humankind descended once again into a Dark Age, and if just one copy of his Encyclopédie survived, civilization could be reconstructed from reading its pages.
A good deal of its content concerned technical issues, such as shoe-making or glass blowing. But other articles addressed political and religious ideas. These are what got the Encyclopédie contributors into legal trouble. The Catholic church and the monarchy were not happy about the generally deist and republican leanings of its authors.
And there were a lot of authors. Most of the leading philosophes wrote one or another of the entries. Louis de Jaucort wrote some 17,000 of them — about a quarter of the total. Each of the contributors wrote about his specialties. D’Alembert, who was a mathematician, wrote most of the math entries. Louis-Jean-Marie Daubenton took on natural history. Jean-Jacques Rousseau wrote about music and political theory. Voltaire on history, literature and philosophy.
All under the editorship of Diderot and d’Alembert, and, after 1759, by Diderot alone.
Diderot divided all of human knowledge into three parts: memory; reason, and imagination. In his Preliminary Discourse to the Encyclopedia of Diderot, d’Alembert explained these as “memory, which corresponds with History; reflection or reason, which is the basis of Philosophy; and imagination, or imitation of Nature, which produces Fine Arts. From these divisions spring smaller subdivisions such as physics, poetry, music and many others.”
In fact, d’Alembert asserts, all of human knowledge is really just one big thing: a unified “tree of knowledge,” which if we could grasp, would explain everything with a single simple principle, which rather prefigures the unified field theory of modern physics.
It would be hard to overemphasize the influence of the Encyclopédie in the 18th century and in the political changes of France up to and through the Revolution. The Encyclopédie disparaged superstition, of which they counted religion as an example, and it saw the purpose of government to be the welfare of its people and the authority of government to be derived from the will of its citizens. The king existed, they said, for the benefit of the people, and not the people for the benefit of the monarchy.
It’s no wonder, then, that the church and the aristocracy tried to suppress parts of the Encyclopédie, and that many of its authors spent time in prison.
Its successor, the Enyclopedia Britannica, wrote of Diderot’s labors, “No encyclopedia perhaps has been of such political importance, or has occupied so conspicuous a place in the civil and literary history of its century.”
Beyond the Encyclopédie, Diderot continued as a freelance writer, as an art and theater critic, a playwright, novelist, political tract writer and freethinker.
But despite his fame and productivity, Diderot never made much money from his work, and when Russian empress — and groupie to the philosophes — Catherine the Great, heard of his poverty, she offered to buy his extensive library, paying him an enormous sum for the books and as salary for his employment as librarian to his own collection.
In 1773, Diderot traveled to St. Petersburg to meet Catherine. Over the next five months, they talked almost daily, as Diderot wrote, “almost man-to-man,” rather than monarch to subject.
Catherine paid for his trip in addition to his annuity and in 1784, when Diderot was in declining health, Catherine arranged for him to move into a luxurious suite in the rue de Richelieu, one of the most fashionable streets in Paris. He died there a year later at the age of 70.
Despite her admiration for Diderot and his revolutionary ideas, Catherine ignored all of them in her own autocratic rule of Russia. But Diderot and his Encyclopédie pointed the way to the Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, the triumph of democracies, and even the American Declaration of Independence and Constitution.
According to philosopher Auguste Comte, Diderot was the foremost intellectual in an exciting age, and according to Goethe, “Diderot is Diderot, a unique individual; whoever carps at him and his affairs is a philistine.”
—————————————————————-
“On doit exiger de moi que je cherche la vérité, mais non que je la trouve.”
“I can be expected to look for truth but not that I should find it.”
—Denis Diderot, Pensées Philosophiques (1746)
————————————————————
When I was a young man, more than a half century ago, I had a simple ambition: To know everything. I suppose I was thinking mainly of facts; I would have no inkling of anything that couldn’t be named and catalogued. I wanted to read everything, name every bird and wildflower, every tree and understand every philosopher. I read all the poetry I could find, listened to all the symphonies and quartets and attempted to ingest all of astronomy and physics and history. Yes, I was an idiot.
As early as the second grade, I believed that when I got to college, then I would finally have access to everything. And so, when I went to Guilford College in North Carolina, I couldn’t wait and in my first semester, I signed up for 24 credit hours of courses. I had to get permission from the dean for the extra hours above the normal 18 that for most students was a full course load. I grabbed Ancient Greek language, astronomy, Shakespeare, the history of India, esthetics, music theory — and over four years, everything I could think of.
To my surprise and disappointment, not all of it was as edifying as I had hoped and not all the professors as brilliant as I had imagined. Still, it was a lot better than high school.
What I sought was knowledge that was encyclopedic, encompassing all there was to know. Yes, I know now that all this was silly. I was young, naive and idealistic. Always a poor combination.
The match that ignited this quest was probably the first actual encyclopedia I had. When I was in grade school, our next door neighbor, who worked for Doubleday publishing in New York, gave us boxes of books, mostly old, and that included a full set of Compton’s Pictured Encyclopedia — probably the set our neighbor had when he was a boy. It dated from the 1930s and had great imagination-burning articles on such things as “The Great War,” dirigibles, and steam locomotives. The endpapers of each volume included illustrations of such things as elevated roads, autogyros, and speedboats.
It didn’t matter that much in the set was out of date. It was a multi-volume key to unlock a whole world.
Later, our parents bought a more up-to-date Funk and Wagnalls encyclopedia, purchasing a single volume each week through a promotional deal at the A&P supermarket. It was a much cheaper production, on cheaper paper, with blank endpapers, but at least it included the Second World War.
All through my childhood and adolescence, I would grab a volume and randomly read entries. I would pore over its pages, reading it all for fun. When I had to write a term paper in high school, I did my research in our Funk and Wagnalls.
I can’t say I read every article in the whole encyclopedia, but I may have come close.
And as I grew, my ambition grew: I wanted, more than anything, to own the two great compendia of all human knowledge: The Oxford English Dictionary and the Encyclopedia Britannica. Both were well out of my price range, but I lusted, the way most boys my age lusted after Raquel Welch.
Years later, after college, the OED was published in a two-volume compact form, with microscopic print and a magnifying glass to read it, and I managed to get a copy through signing up for a book-of-the-month club. I still have it, and I still browse through it to find random words, their histories and the curious way language changes over the years.
The Britannica took longer. The Encyclopædia Britannica, or, A Dictionary of Arts and Sciences, compiled upon a New Plan, was published in Edinburgh first in 1768, as an answer to Diderot’s Encyclopédie. At first, it was bound in three equally sized volumes covering: Aa–Bzo; Caaba–Lythrum; and Macao–Zyglophyllum. There have been 15 editions since, but each edition was continually updated, making the Britannica a constantly evolving entity. It was briefly owned by Sears and Roebuck, and eventually migrated to the University of Chicago. Currently it is privately owned and only available digitally. They stopped printing it in 2010.
It wasn’t until I was in my 30s, when working as a teacher in Virginia, I found an old used set of Britannicas at a giant book sale held annually in the city’s convention center. It was an 11th Edition version — still the standard as most desirable edition. I felt like Kasper Gutman finally getting his hands on the Maltese Falcon. But when I unwrapped my prize, it was, in fact, the real thing.
It sat, in pride of place, on my bookshelves, more as trophy than anything else. And when we moved to Arizona, I had to give it up in the great divestment of worldly goods necessary to truck our lives across a continent. I hated to give it up, but had to admit, I wasn’t using it as much as I had expected. I had an entire library of other books that I could consult.
Then, in Arizona, I came across a more recent edition of the Britannica for sale at Bookman’s, a supermarket-size used book store in Mesa, Ariz. It was the version divided into a “macropedia” and “micropedia.” I bought it to replace the earlier version I had once coveted.
I have never warmed to this version of the encyclopedia — a smaller set with simpler, introductory articles about a wider range of subjects, and a longer set with in-depth scholarly articles about a smaller range of more commonly referenced subjects. It felt dumbed down — and worse, confusing, because you could never quite tell if you should first consult the micro- or the macro- section of the series.
But at least, I still owned a Britannica, and felt that somehow, I possessed, if not the actual knowledge of the universe, at least access to it.
The end of Britannica was also the end of my obsession with it. With the advent of Wikipedia, I no longer needed to shuffle through pages of multiple volumes, sort through indexes, or cross-reference material. In researching a story for my job as art critic with the newspaper, I could just go online and get the birth date of Picasso or the list of art at the Armory Exhibit of 1913. Wikipedia was easier to use, and for my purposes, just as accurate as my beloved Britannica.
And so much easier to use. I cannot now imagine being a writer without Wikipedia. If I need a date or check spellings, it is instantly available.
And just as I spent time as an adolescent swimming through my Compton’s or Funk and Wagnalls, reading random articles for the fun of it, I now spend some portion of my time sitting in front of my computer screen hitting the “random article” button on Wikipedia to read about things I wouldn’t have known to be interested in. Lake Baikal? Yes. Phospholipidosis? It is a “lysosomal storage disorder characterized by the excess accumulation of phospholipids in tissues.” De Monarchia? A book by Dante Alighieri from 1312 about the relationship of church and state, banned by the Roman Catholic Church. I know of some politicians who might profit by reading Dante.
It’s fun picking up random bits of information like this. But it also demonstrates why my interest in owning all the world’s knowledge in book form has evaporated.
First, the cosmos is infinite and packing 20 volumes of an encyclopedia with information about it is really like taking a teacup to the ocean. Second, knowledge keeps changing and growing. What we thought we knew a hundred years ago has been replaced by more complete data and theory — and so knowledge is not so much a teacup as a sieve.
Then, there is the even more knotty problem, that knowledge isn’t even the most important part of understanding. Facts are good, and I wouldn’t want to be without them, but infinitely more essential is the interrelationship between them; the complexity of human mind as it interacts with what it knows, or thinks it knows; the moiling stew that is the mix of thought and emotion; the indistinct borders of learning and genetic inheritance; the atavistic tribalism that seems to overcome any logic; the persistence of superstition, magic and religion in how we understand our Umwelt; and ultimately, the limitations of human understanding — how much more is there that we not only don’t know, but cannot know, any more than a goldfish can understand nuclear fission.
The reality of our existence is both infinite and unstable. Trapping it in print is an impossibility. It swirls and gusts, churns and explodes. Any grasping is grasping handfuls of air. We do our best, for the nonce, and must be satisfied with what we can discern in the welter.
I think of Samuel Johnson’s heartbreaking preface to his 1755 Dictionary, which every thoughtful person should read and lock to mind. “To have attempted much is always laudable, even when the enterprise is above the strength that undertakes it: To rest below his own aim is incident to every one whose fancy is active, and whose views are comprehensive; nor is any man satisfied with himself because he has done much, but because he can conceive little. … When I had thus enquired into the original of words, I resolved to show likewise my attention to things; to pierce deep into every science, to enquire the nature of every substance of which I inserted the name, to limit every idea by a definition strictly logical, and exhibit every production of art or nature in an accurate description, that my book might be in place of all other dictionaries whether appellative or technical. But these were the dreams of a poet doomed at last to wake a lexicographer. … I saw that one enquiry only gave occasion to another, that book referred to book, that to search was not always to find, and to find was not always to be informed; and that thus to pursue perfection, was, like the first inhabitants of Arcadia, to chase the sun, which, when they had reached the hill where he seemed to rest, was still beheld at the same distance from them.”
Amen.